bestcybercasinos ≡ Offers Slots Sign On Tips Casino online pokies real money AustraliaThis article helps…
How Leaders Impact Employee Motivation and Performance
“Leadership is absolutely about inspiring action, but it is also about guarding against mid-action.” – Simon Sinek.
Employee motivation is crucial for organizational success. Yet many leaders need help to motivate their teams. A disengaged workforce leads to reduced productivity and higher turnover.
The year 2024 has brought about a number of emerging trends in the arena of employee motivation and performance. One of the most significant trends is the increasing focus on flexible work arrangements that promote a blend of remote and in-office collaboration. This trend is being driven by the need to accommodate the changing needs of the modern workforce, and it is expected to continue to gain momentum in the coming years.
Another important trend is the growing emphasis on holistic well-being initiatives that prioritize mental health support and wellness programs. This is in recognition of the fact that a balanced work environment is essential for promoting employee engagement and driving sustained performance.
Finally, personalized professional development plans and real-time feedback mechanisms are also gaining prominence as effective tools for enhancing employee engagement and driving sustained performance. These tools are designed to help employees identify areas for improvement and provide them with the support they need to achieve their goals, while also giving employers valuable insights into their performance and progress.
As we delve into how leaders can effectively influence their teams, it’s essential to integrate the latest insights to stay ahead in the corporate realm.
Before moving forward with a task or project, it is crucial to have a clear understanding of motivation and its significance. Therefore, let us begin by delving into the concept of motivation and its impact.
Motivation and Its Importance

In the corporate landscape, addressing challenges related to recruitment, retention, and minimizing turnover is paramount for sustained success. A key factor in overcoming these hurdles lies in the strategic cultivation of employee motivation, which directly impacts morale.
Successful corporations recognize that motivated employees are not only instrumental in enhancing productivity but also play a crucial role in attracting and retaining top talent. A motivated workforce requires less oversight, contributing to a more efficient and harmonious work environment. By fostering high morale, companies can significantly reduce churn rates and cultivate a positive organizational culture that resonates with both current and prospective employees.
Conversely, organizations grappling with low motivation risk facing difficulties in recruitment efforts and struggle to retain their valuable workforce. A lack of enthusiasm among employees can contribute to higher turnover rates, negatively impacting the overall health and reputation of the company.
To effectively tackle these challenges, corporations should devise targeted strategies aimed at boosting employee motivation. Such initiatives may include recognizing and rewarding achievements, providing opportunities for professional development, and creating a supportive workplace culture that values the well-being and job satisfaction of its employees. By proactively addressing these motivational aspects, corporations can enhance recruitment outcomes, reduce turnover, and ultimately elevate the overall morale within the organization.
Types Of Motivation
| Type of Motivation | Description |
| Intrinsic Motivation | Refers to the internal drive from personal satisfaction, enjoyment, or accomplishment in the work itself. Leads to self-directed, engaged, and proactive employees. This intrinsic motivation becomes a cornerstone for sustained employee engagement, reducing the likelihood of turnover. |
| Extrinsic Motivation | Derived from external rewards or incentives like bonuses, promotions, or recognition for achieving goals. Effective for short-term objectives and when paired with other factors. |
| Financial Motivation | Recognize the critical role of competitive salaries, bonuses, and profit-sharing plans in attracting and retaining talent. To address churn, ensure that financial motivation strategies are not only competitive but also tied to individual performance. Transparent and fair financial recognition contributes significantly to overall employee satisfaction and long-term commitment. |
| Social Motivation | Based on interpersonal relationships and interactions in the workplace. By fostering a positive team culture, implementing recognition programs, promoting mentorship, and encouraging open communication, leaders can make employees feel valued and connected. This sense of belonging and camaraderie enhances motivation, engagement, and ultimately reduces churn. |
| Achievement Motivation | It involves setting challenging goals and providing opportunities to achieve them. By establishing clear objectives, leaders can motivate their teams to surpass targets, improve performance, and accomplish tasks. Regular feedback and recognition play a vital role in enhancing achievement motivation, as they provide employees with a sense of progress and accomplishment.. |
| Growth and Development Motivation | Focuses on providing opportunities for personal and professional growth through training, job rotations, mentoring, or further education support. Increases motivation, engagement, and commitment. |
Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory
Frederick Herzberg’s two-factor theory, also known as the motivator-hygiene theory, attempts to explain satisfaction and motivation in the workplace.
Herzberg suggested that more than meeting the lower-level needs of employees, motivation and satisfaction are needed in the long term. Instead, he proposed a two-factor model based on hygiene factors and motivator factors.
Hygiene Factors
Hygiene factors describe the work environment. When they are adequate, workers will be satisfied. However, they do not lead to long-term satisfaction or motivate employees to higher performance. Hygiene factors include:
- Company Policies
- Supervision
- Relationship With The Manager
- Work Conditions
- Salary
- Status
- Security
According to Herzberg, insufficient hygiene factors can create job dissatisfaction, but having optimal hygiene factors does not motivate or satisfy employees.
Motivators
Motivator factors are those aspects of work that provide deep satisfaction, fulfill employees’ higher needs, and encourage them to perform superiorly. These include:
- Achievement
- Recognition
- Challenging Work
- Increased Responsibility
- Opportunities For Growth
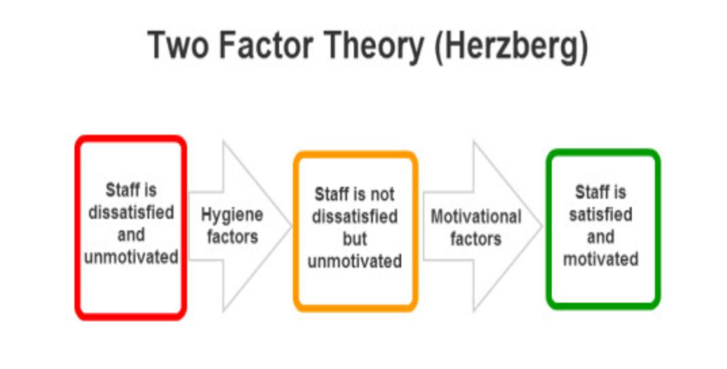
According to the two-factor theory, motivators are the conditions that genuinely encourage employees to try harder. Managers should focus on improving motivators to increase productivity and employee satisfaction.
This model recognizes that both motivation and hygiene factors are essential for overall job satisfaction.
However, Herzberg posited that they function independently and are not opposites of one another. Eliminating dissatisfying hygiene factors does not automatically create employee motivation. Likewise, increasing motivators does not diminish dissatisfaction caused by poor hygiene factors.
Leader’s Role in Motivation
The influence of effective leadership on employee motivation cannot be overstated. The role of leaders in employee motivation is constantly evolving as new challenges emerge in the workplace. While many are familiar with traditional motivational techniques, today’s leaders must adapt to modern issues like quiet quitting and AI anxiety. Here are some insights on leading with empathy in uncertain times:
- Encouraging Autonomy and Empowerment
Empowering employees to make decisions and take ownership of their work not only helps them feel valued but also promotes a sense of responsibility and motivation. Leaders who delegate tasks and provide opportunities for growth and development create an engaged and motivated workforce.
- Quiet Quitting Response
With quiet quitting, employees do their basic job duties without going above and beyond. Leaders should avoid knee-jerk reactions to shame quiet quitters. Instead, approach individuals with curiosity and ask what would excite their engagement.
Listen without judgment and identify roadblocks to motivation like burnout or unclear expectations. Reframe extra efforts as optional ways to grow, not mandatory. Quiet quitting is a symptom – treat the root causes with compassion.
- Emphasizing Up skilling and Reskilling
Leaders can play a pivotal role in creating a culture of continuous learning. Encouraging employees to acquire new skills and supporting their professional development helps them adapt to technological advancements and remain relevant in their roles.
Many employees worry about artificial intelligence and automation replacing their jobs. Leaders should be transparent about how technology may impact jobs. They should also focus on up skilling employees and emphasizing the human skills that AI cannot easily replicate. This helps give employees a sense of security about their long-term value.
- Fostering Collaboration between Humans and AI
Rather than viewing AI as a threat, leaders can help employees see it as a tool that enhances their capabilities. By emphasizing the collaborative potential of humans and AI, leaders can alleviate fears, promote innovation, and create a dynamic work environment.
- Transparent Communication about AI Implementation
Leaders should proactively communicate the role of AI in the organization and how it complements employees’ skills and expertise. By providing clear information and addressing concerns, leaders can build trust and ensure a smooth transition.

- Desire for flexibility
Many employees today want more flexibility and work-life balance. Leaders should implement policies like flexible work hours, job sharing, and remote work options whenever possible.
They should also set an example by not sending emails outside of work hours and taking their own time off. This promotes a culture where work-life balance is valued.
- Leading by Example
Leaders are role models for their teams. By embodying the values and behaviors they expect from their employees, leaders can inspire and motivate through their actions. When leaders consistently demonstrate a strong work ethic, resilience, and a positive attitude, they set the tone for a motivated and high-performing team.
- Linking Employee Engagement to Organizational Success
There is a direct correlation between employee engagement and organizational success. Highly motivated and engaged employees tend to be more productive, loyal, and willing to go the extra mile for the company.
By focusing on factors like meaningful work, growth opportunities, recognition, a supportive work environment, and fair compensation, leaders can significantly boost employee engagement and, consequently, the company’s performance.
Employee Engagement and Motivation Factors.
Modern workplaces are dynamic environments, so understanding the key elements that drive employee engagement and motivation is crucial. Let’s delve into the factors that are pivotal in shaping an inspired, committed, and high-performing workforce.
2024 Workplace: A Relationship Reset.
The year 2024 marks a significant shift in the employer-employee relationship. A major factor contributing to this change is the evolution of work locations and styles.
With a notable decrease in on-site working and an increase in remote or hybrid models, the way employees engage with their work and organizations has transformed dramatically.
However, location isn’t the only driving force. Gallup highlights that the management style holds four times more influence over employee engagement and well-being than the work location itself.
Leaders need to adapt their strategies to these changing dynamics, focusing on building solid relationships and a supportive culture within their teams.
Global Stress and Engagement Trends
An intriguing paradox emerges in 2024: while employee engagement is on the rise globally, stress levels continue to soar, especially in North America.
Leaders must navigate this delicate balance, fostering an environment that supports employee well-being while maintaining high engagement levels.
Decline in Organizational Mission
A concerning trend is the decrease in employees feeling connected to their organization’s mission and purpose. This connection is a crucial driver for going beyond basic job demands and striving for excellence.
Leaders must find innovative ways to reinforce this sense of purpose within their teams.
Restoring Trust in Leadership:
The pandemic era saw a decline in trust in organizational leadership. As we move forward, leaders must rebuild this trust. Clear communication, support for change, and inspiring confidence are pivotal in gaining back employee trust.
The Challenge for Managers
Managers are facing an unprecedented squeeze due to increased responsibilities and organizational changes. Their struggles directly impact their teams, as they play a critical role in employee engagement.
Leaders must provide adequate support and training to managers, helping them navigate these challenges effectively.
Engaging with technology
As we advance into 2024, the integration of artificial intelligence and automation in employee engagement strategies is becoming increasingly important. This integration allows for a seamless execution of engagement initiatives and a more data-driven approach to enhancing employee efforts.
Building a United Workforce
The concept of community in the workplace is evolving with the rise of digital platforms and remote work. Leaders are now focusing on creating global communities that share common goals and values, transcending geographical boundaries.
This shift demands an inclusive approach, uniting employees around shared objectives and a strong company culture.
The New Norm for Continuous Learning
Traditional feedback models are making way for endless, organic feedback loops. Leaders need to embrace this shift, ensuring that feedback directly contributes to learning and development. This approach fosters a culture of continuous improvement and positive mental health.
Case Studies of Motivation Tactics
Motivation strategies vary based on company culture and goals. Here are some real-world examples:
Patagonia
Patagonia, an outdoor apparel company, champions environmental activism by offering paid volunteer time for ecological causes and funding employee-led initiatives.
They also emphasize work-life balance with policies like sabbaticals, flexible schedules, and on-site childcare, connecting employees’ work with their values and well-being.
Toyota
Toyota fuels employee motivation through its core philosophy of continuous improvement (“kaizen”). Their renowned Toyota Production System empowers workers with autonomy, fosters a culture of respect and trust, and encourages teamwork towards shared goals. Job security, competitive compensation, recognition, and investment in training further solidify employee engagement, propelling Toyota as a leader in the automotive industry.
Mutombo Coffee
Mutombo Coffee could tap into non-monetary motivators to engage employees. Company retreats, peer mentoring programs, and social impact projects can fulfill employees’ needs for relatedness, growth, and meaning.
Clear communication of how employees’ roles impact customers provides purpose. With the right intrinsic motivators, Mutombo Coffee can increase productivity and loyalty.
Conclusion: Leading with Purpose
In the ever-evolving corporate world, the role of leaders in influencing employee motivation and performance is more crucial than ever. By understanding the key trends, adapting to new workplace dynamics, and learning from real-world examples, leaders can effectively boost employee engagement and drive organizational success.
Remember, motivated employees are not just more productive and engaged; they are the heart of an organization’s growth and innovation. Leaders who prioritize employee motivation and engagement are paving the way for a more dynamic, committed, and successful workforce.
As we wrap up this exploration of leadership and employee motivation, we invite you to explore the rich flavors and community-driven mission of Mutombo Coffee. Discover how our commitment to quality and sustainability mirrors the principles of effective leadership and employee engagement.
Founded by NBA Hall of Famer and global humanitarian Dikembe Mutombo and social investor Bob Bush, Mutombo Coffee was created to amplify the mission and values of our corporate partners while supporting African and Latin American farmers.
Contact us now to learn more!
References